|
Relays are electro-mechanical devices used for switching. Relays are used to make the signaling logic circuits
in the interlocking plants. They consists of one or two magnetic coils (electro
magnets) and a set of contacts. Magnetic System
The magnetic system of the relay illustrated below (JRK 10 type)
consists of a cylindrical iron core with coil (pale blue near the bottom), two
pole pieces and an armature. Larger relays (JRK 11) have two iron cores united
at the rear with a yoke and the front end being provided with pole pieces. The
armature extends across both pole pieces. 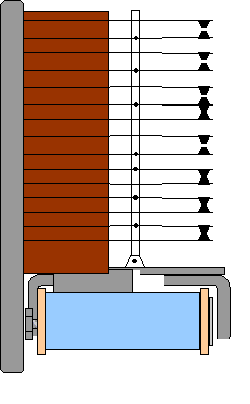 Iron core, pole pieces and armature
are made out of iron with excellent magnetic properties. The armatures are so balanced
that the vibration on the unit will not affect the relay operation. [Move the
mouse over the relay to activate it!] Iron core, pole pieces and armature
are made out of iron with excellent magnetic properties. The armatures are so balanced
that the vibration on the unit will not affect the relay operation. [Move the
mouse over the relay to activate it!]
Contacts
The relay contacts can be classified into four types. A relay unit will
contain a combination of these types
.
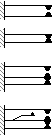 |
Front contact - NO
Back contact - NC
Front/ Back contact
Make before break contact |
The contact springs are made out of
nickel and the contacts tips are silver. The front contacts are of twin contacts
and the back contacts are single contact type. The rear end of the contact
springs are fixed between two blocks of transfer molded carbonate plastic
reinforced with glass fibre. The stationary contact springs are supported
at their free ends by a strip with notches, which limits the spring movement.
The lower end of this strip is attached to the magnet support. The movable
contact springs are guided by an actuating strip which at the lower end attached
by bearings to the armature and at the upper end to the upper most movable
contact spring. The front edge of the actuating strip provided with slots, which
lock the spring and guide the movement of the contacts. The rear end of every
contact spring has eight forked terminals. This provides a very dependable
connections to the plug board terminals, when the relays are plugged in.
|